|
Welcome to the Visual Intelligence Laboratory (VI-Lab) Webpage. My name is Thanapong Intharah. I am an associate professor in Computer Science at the Department of Statistics, Khon Kaen University (KKU). I am the director of VI-Lab which works on applying Machine Learning and Computer Vision to solve real world problems. Many of our projects were spun off as commercialized products: AI for CCTV and AI for Health . I did my PhD at UCL under supervision of Professor Gabriel Brostow. At UCL, I had been working on using Computer Vision to improve Programming by Demonstration, Learning to Automate GUI Tasks from Demonstration (project page). Before joining KKU, I have founded a Deep Tech startup, TinyEpicBrains, where we work on invisible QR code. Currently, I am interested in Computer Vision for 3D data, video data and applications of AI in Healthcare. I am also working on AI enhanced hardwares such as a differential dynamic microscopy and smart-glasses. |

Thanapong Intharah, Ph.D. |
|
Visual domains such as Medical Imaging and Video Analysis are our expertise, but we also worked on Chatbot, NLP, and other Machine Learning domains. The following are list of selected research projects. |
|
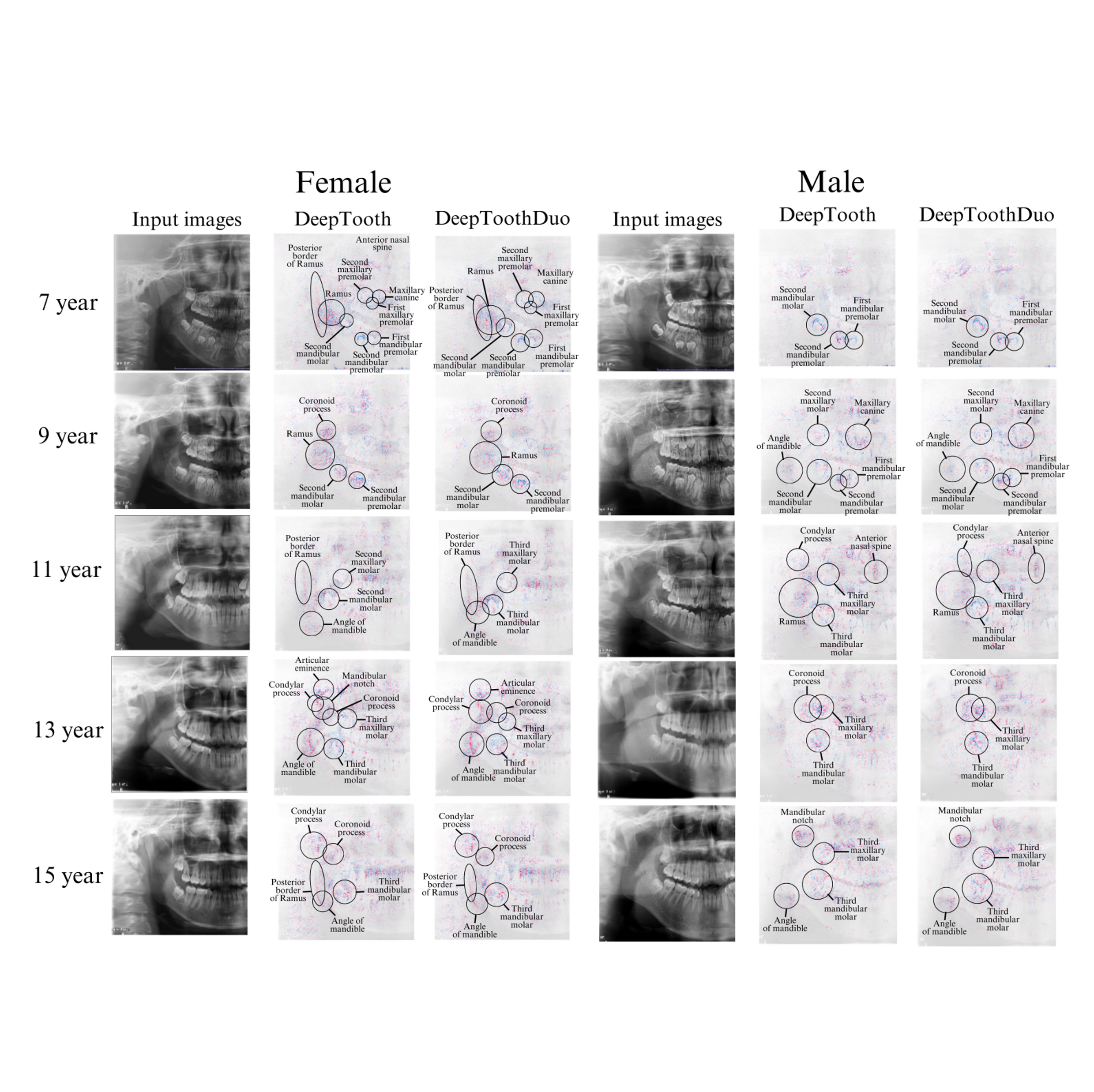
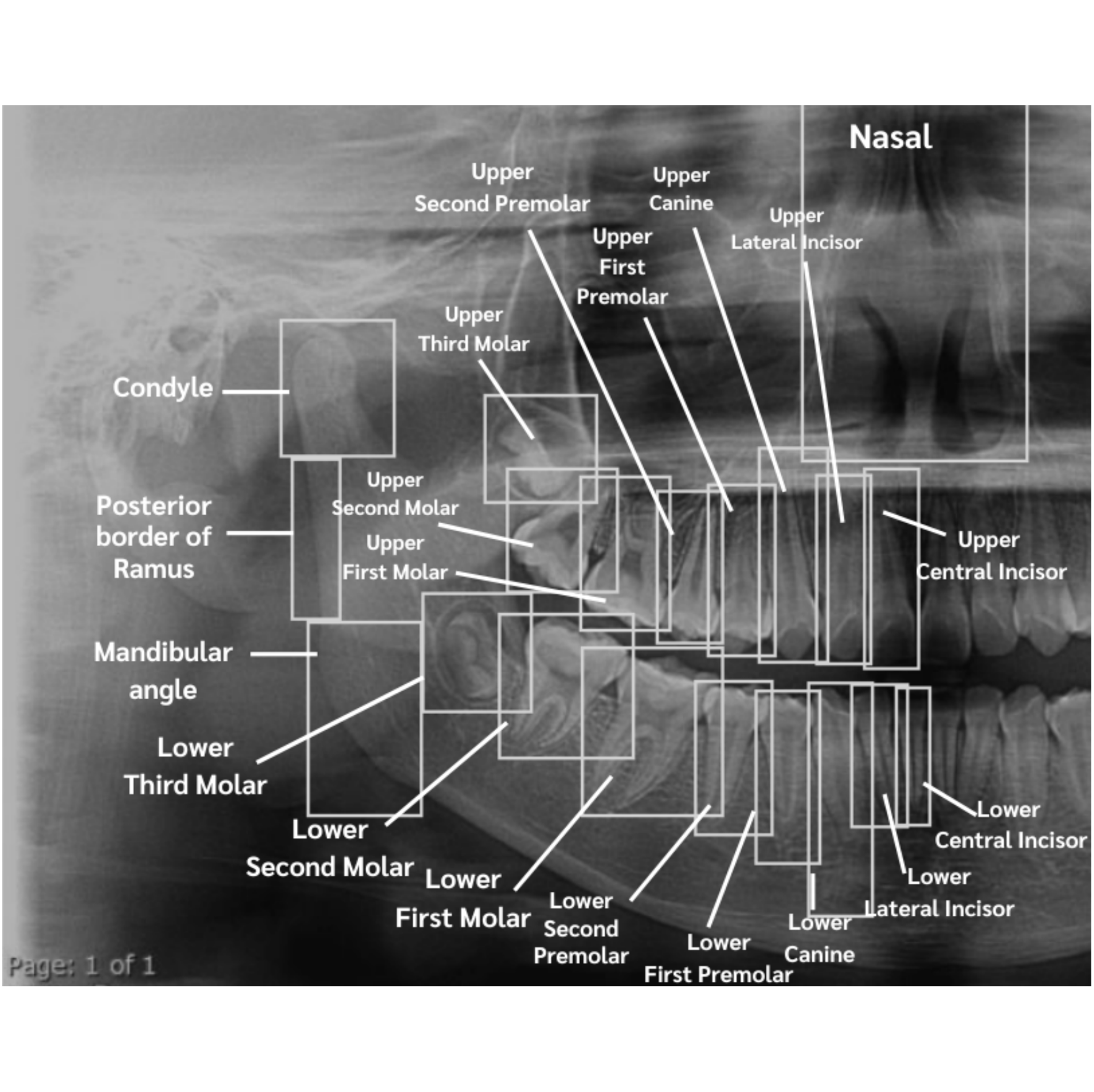
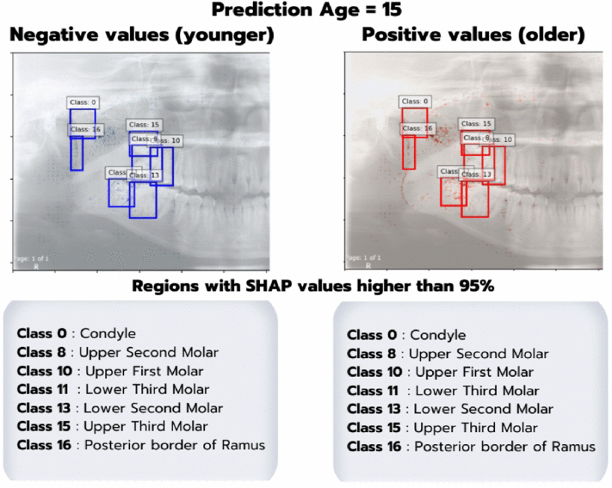
(2024-26) Natthanich Hirunchavarod and Thanapong Intharah [Gold prize: YRSS 2024] [Silver Medal: Higher Education Innovation Awards 2024] This work proposes an explainable AI framework that integrates YOLO and SHAP to reveal anatomically meaningful regions driving age and sex predictions in panoramic dental X-ray images. project page / publication (IEEE Access 2025) |
|
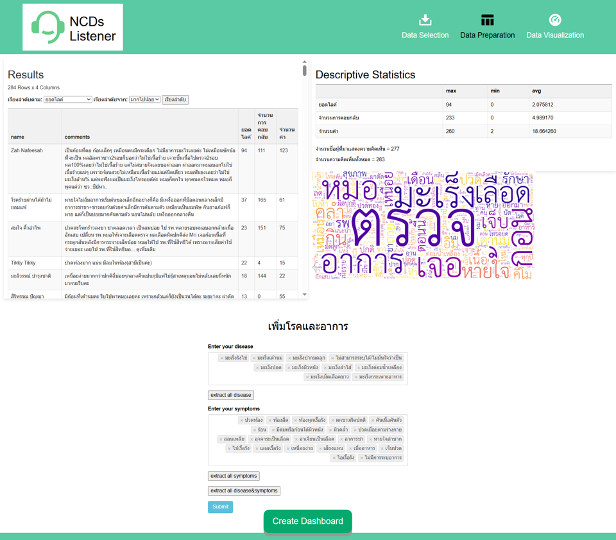
(2024-25) Ratchanont Thippimanporn, Wuttichai Khamna and Thanapong Intharah [Final round: NSC 2024] [xxxx: I-NEW GEN AWARD 2025] NCDs Listener is an open-source social media listening web application that collects, analyzes, and summarizes public discussions about non-communicable diseases to generate actionable insights for patients and researchers. project page / publication (PlosOne2025) |
|
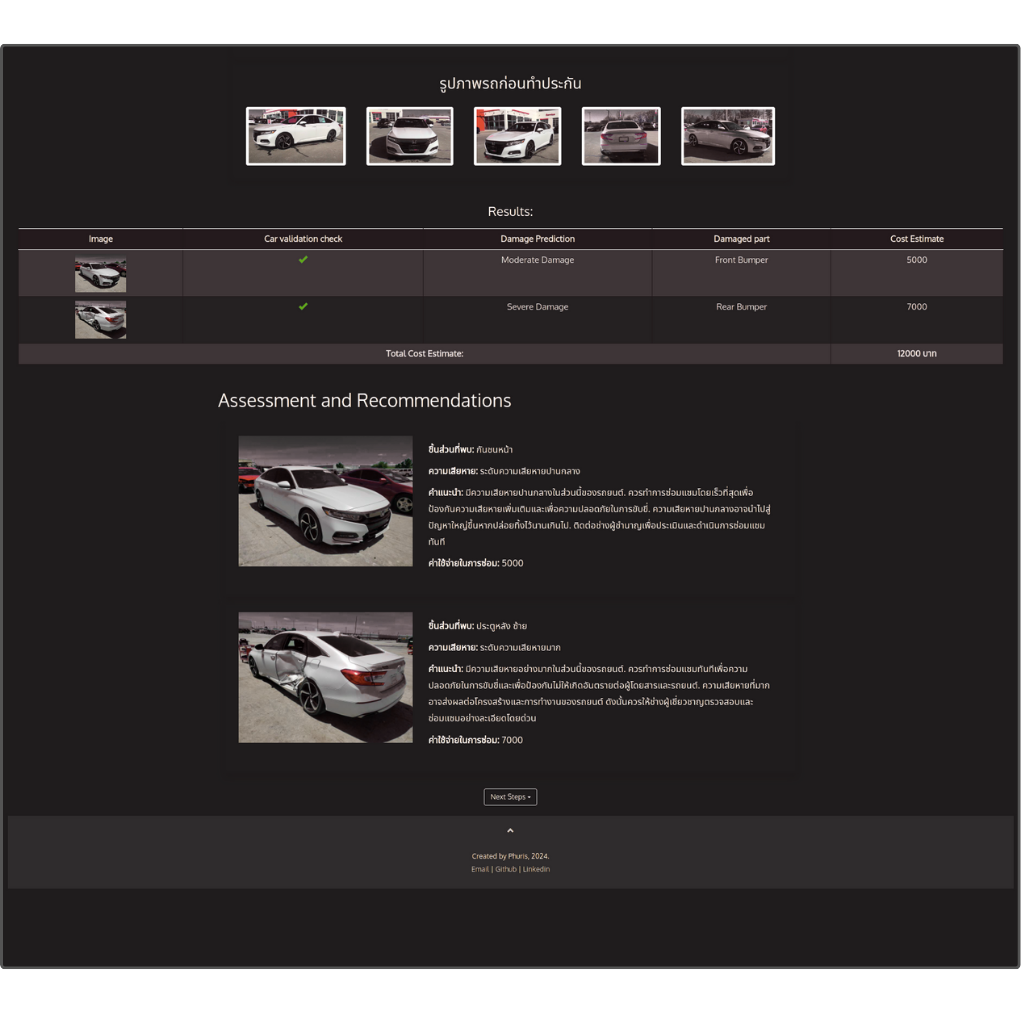
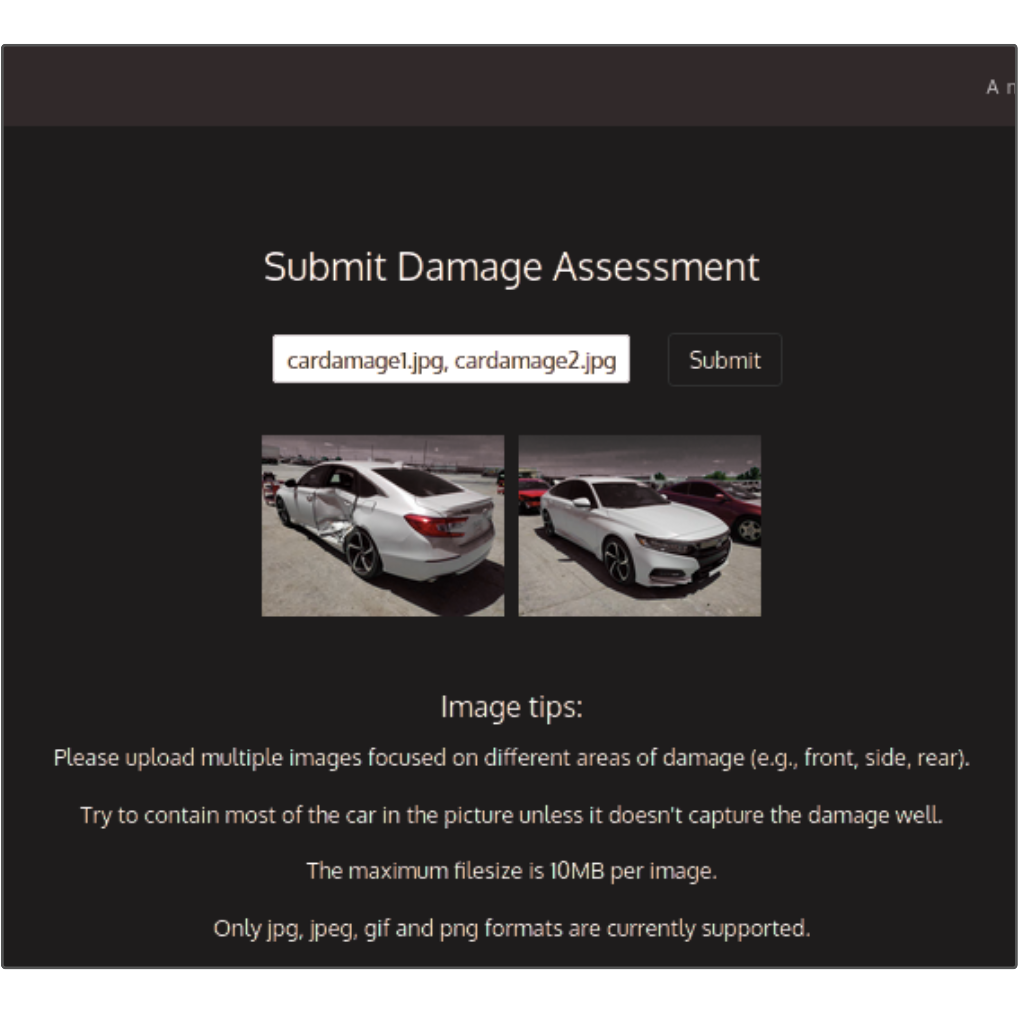
(2024-25) Phuris Kruacharee, Thanaphorn Kanking and Thanapong Intharah [Final round: NSC 2024] [Silver Medal: I-NEW GEN AWARD 2025] DentAnalyzer is a web application that uses deep learning to automatically assess vehicle damage and estimate repair costs from a single image by training on realistic synthetic car images. project page / publication (ITC-CSCC2025) |
|
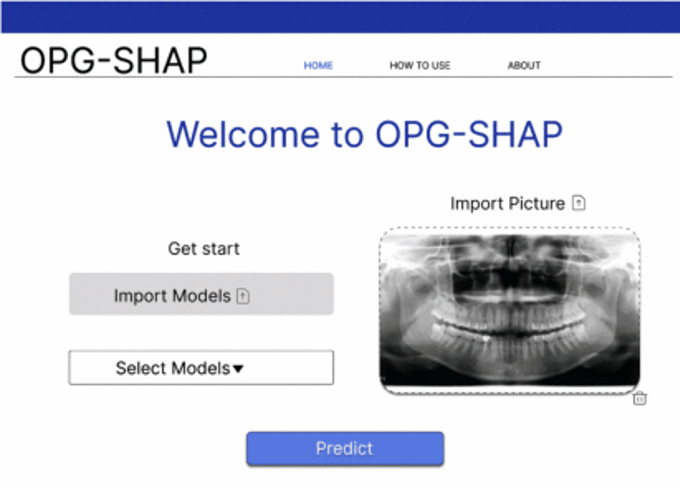
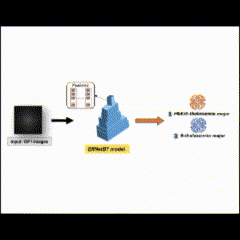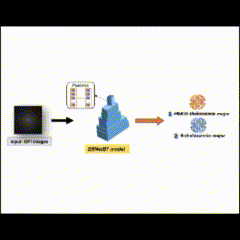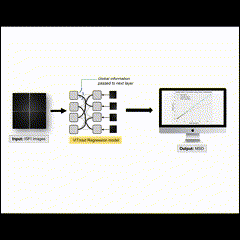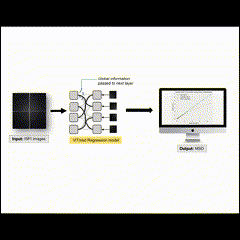
(2024-25) Kwansawan Thongprasant, Lapadrada Dangsungnoen and Thanapong Intharah [Final round: NSC 2024] [xxxx: I-NEW GEN AWARD 2025] [xxxx: YRSS Award 2025] OPG-SPELL is a web application that combines visual and textual explanations (using SHAP values and LLM-generated text) to help users better understand and trust an AI model’s predictions from orthopantomogram images. project page / publication (ITC-CSCC2024) |
|
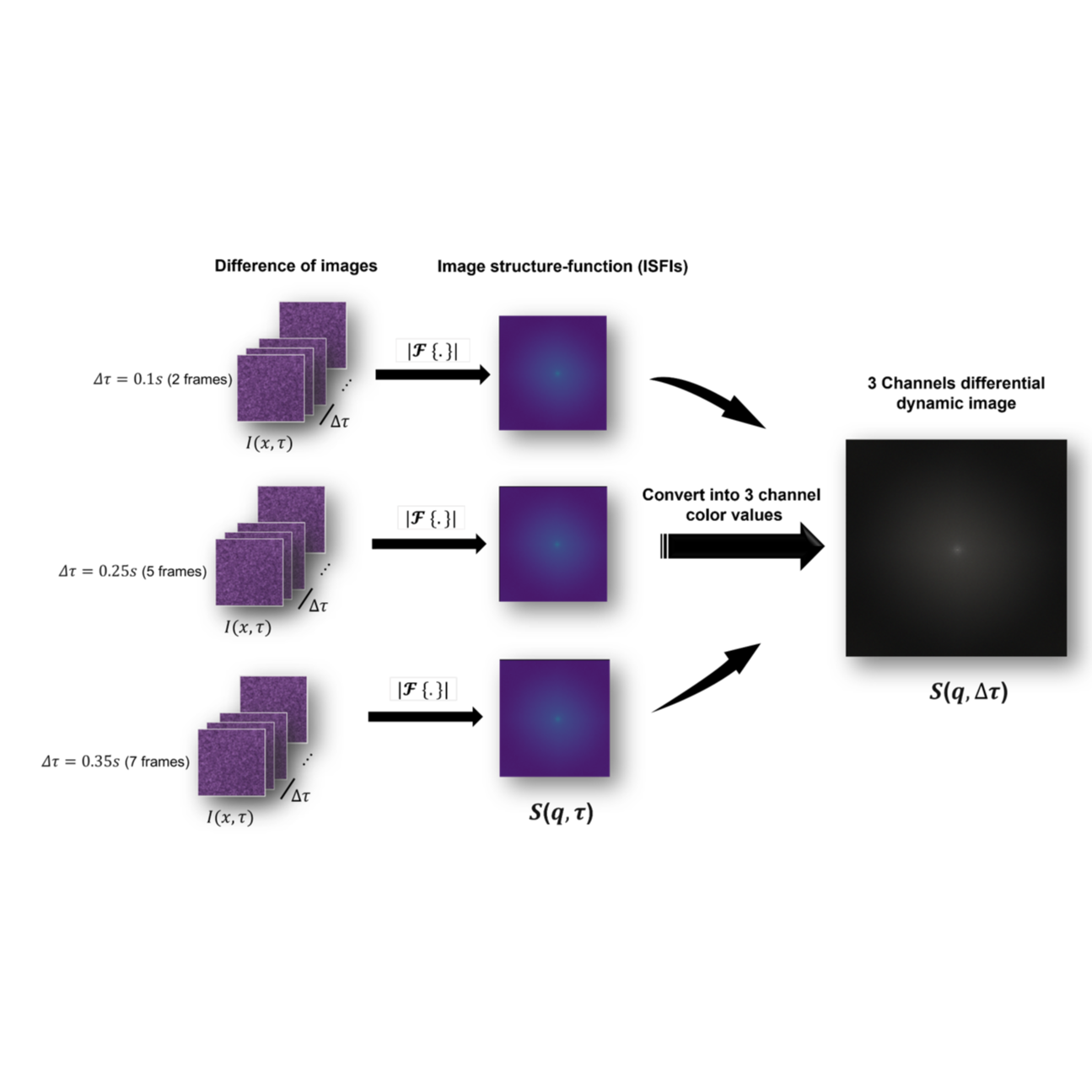
(2023-24) Kannika Wiratchawa, Touchwin Petiwathayakorn, Somdet Srichairatanakool, Pimpisid Koonyosying, Ungkarn Jarujareet and Thanapong Intharah We propose techniques for integrating image structure-function images called ISFI for training deep learning models. project page / publication (ITC-CSCC2024) |

|
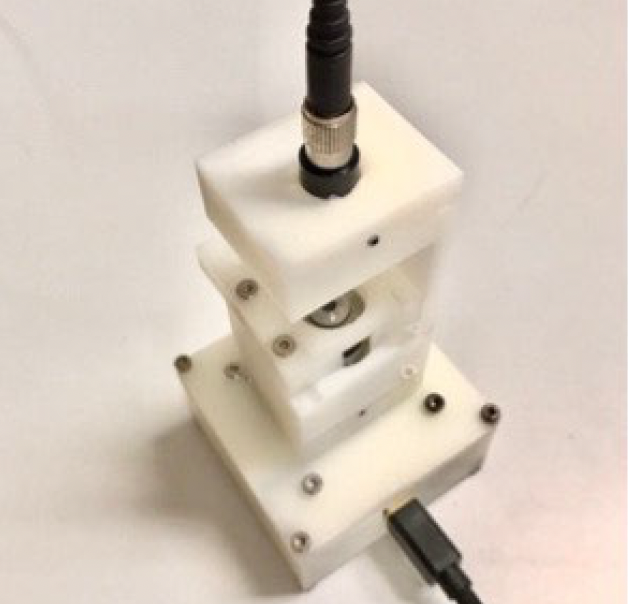
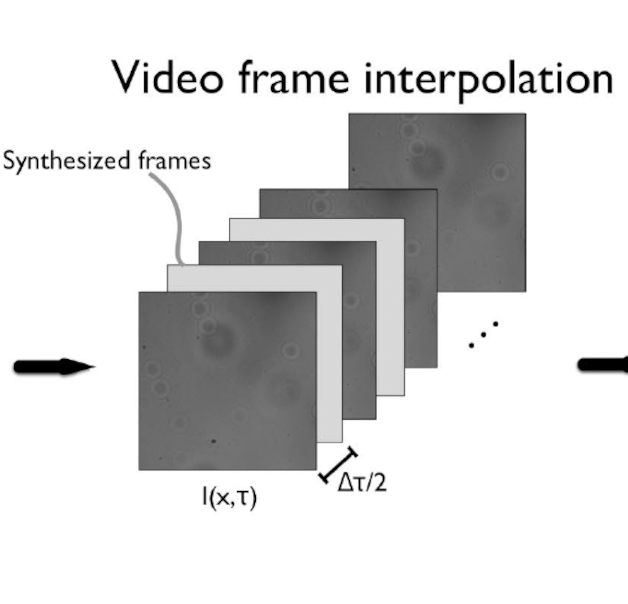
(2022-23) Ungkarn Jarujareet, Kannika Wiratchawa , Piyaphong Panpisut, Thanapong Intharah [PMU-B Grant (B05F650016)] We proposed A DDM device that is enhanced by Deep Frame Interplation Networks. project page / publication |
|
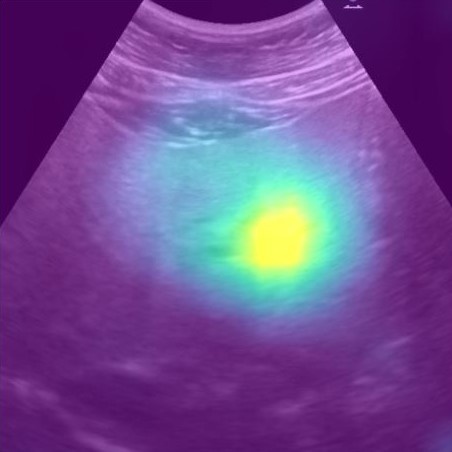
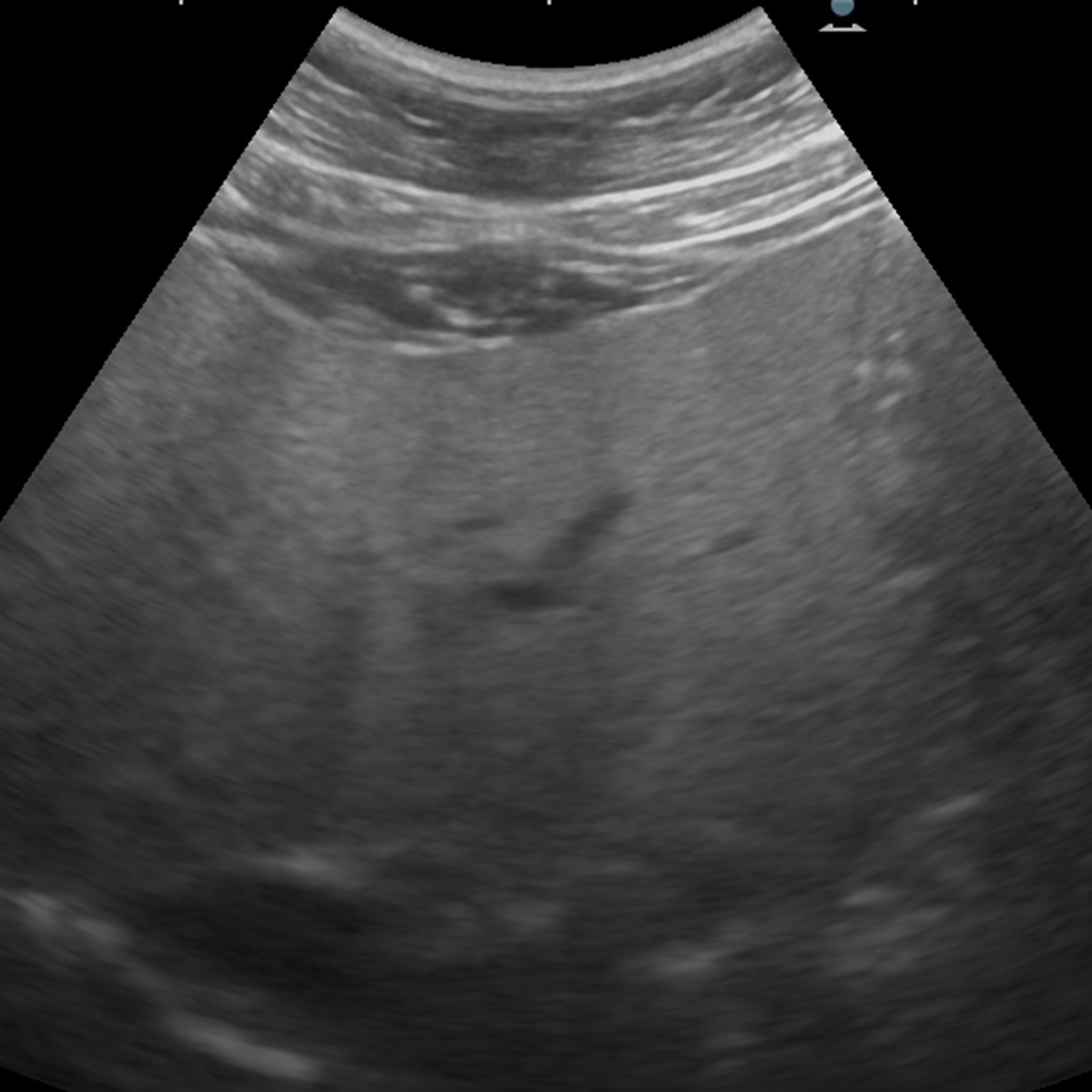
(2020-23) Thanapong Intharah Yupaporn Wanna, Kannika Wiratchawa Prem Junsawang, Anchalee Techasen, Arunnit Boonrod, Attapol Titapun, Vallop Loapaiboon, Nittaya Chamadol, Narong Khuntikeo [1st runner-up: National Innovation Awards 2021(Service Design Category)] [Merit: Thailand ICT Awards 2023 (Inclusion and Community Service)] [Merit: NRCT Invention Awards 2023 (ICT)] [Silver ASEAN Digital Awards 2024 (Digital Innovation)] We developed an AI to assist doctors and radiologists in diagnosing abnormalities in human upper abdominal through ultrasound image. project page / publication |
|
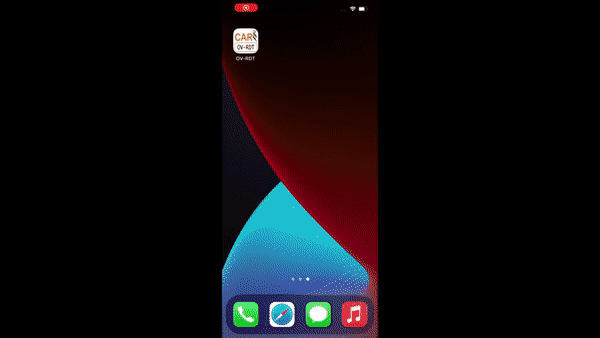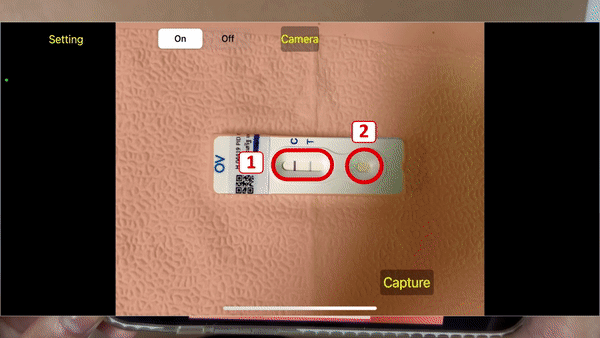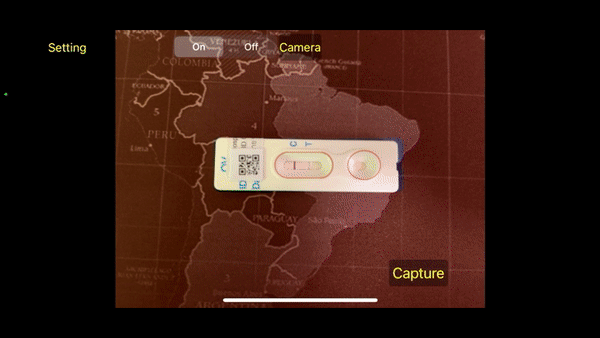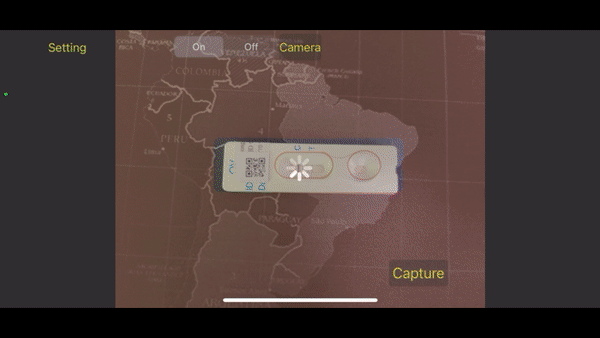
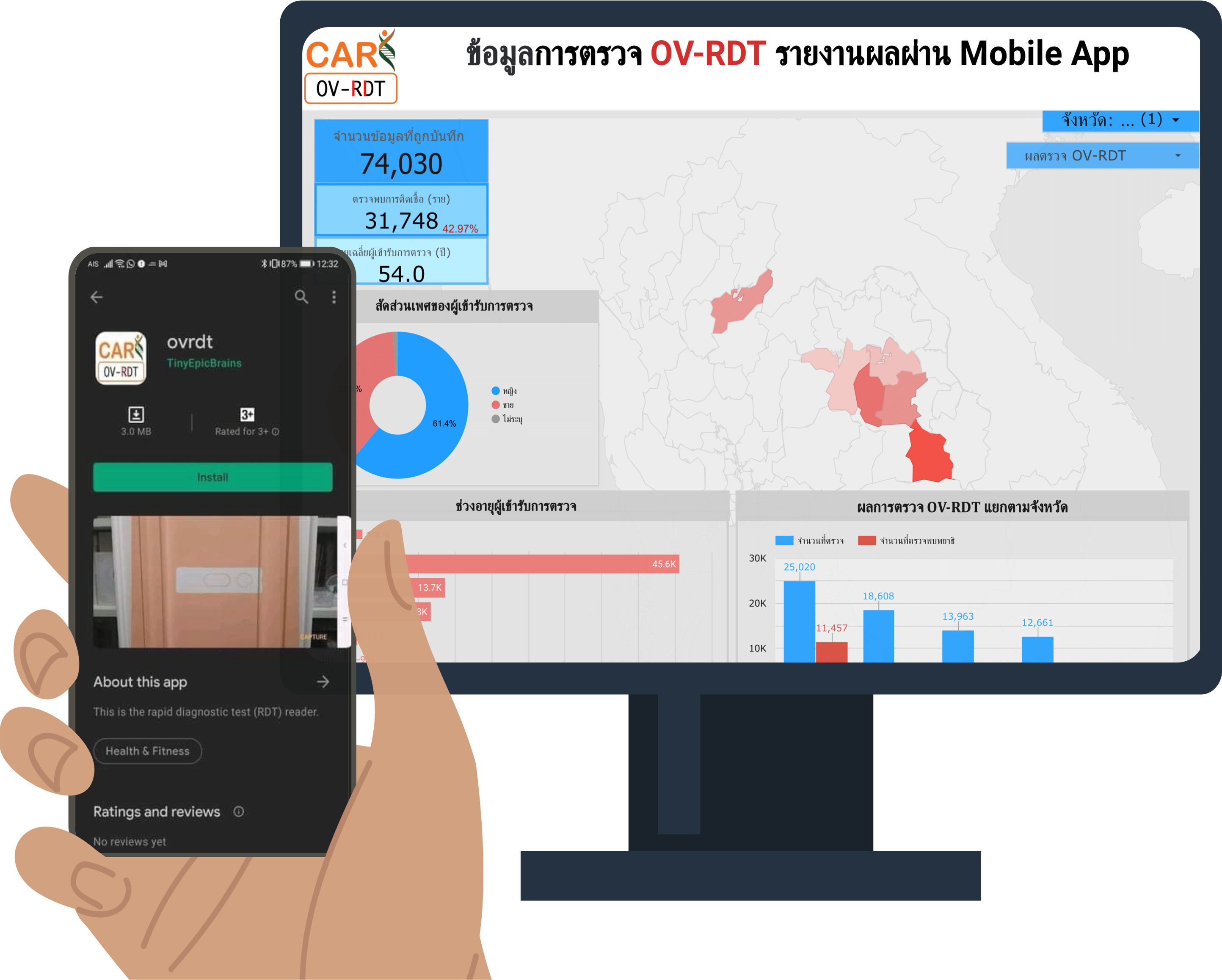
(2021-23) Thanapong Intharah Yupaporn Wanna , Kannika Wiratchawa , Prem Junsawang , Anchalee Techasen , Chanika Worasith , Paiboon Sithithaworn and Narong Khuntikeo [Honorable Mention : NRCT Invention Awards 2023] The OV-RDT platform consists of a mobile app, AI agents, and a dashboard. The mobile app captures and detects OV-RDT test kits via smartphone cameras. AI ensures image quality and identifies Opisthorchiasis presence and severity. Data, including AI diagnostics, are stored and displayed on a dashboard for analysis in epidemiology and patient screening progress. project page / publication |

|
(2024) Natthanich Hirunchavarod, Pornnakanok Phuphatham, Narawit Prathansap and Thanapong Intharah Utilizing deep learning techniques, our project enhances dental care planning by accurately estimating age and gender from panoramic radiographs. Achieving 87.38% gender prediction accuracy and 1.96 years' age estimation error, it offers early diagnosis and forensic applications while ensuring model interpretability. project page / publication (ISBI2024) |

|
(2024) Nattakon Puangkaew, Thanapat Sopon and Thanapong Intharah Valolyze: A Valorant gameplay analytics. Valolyze enables comprehensive analysis of Valorant gameplay from video recordings, empowering players and researchers alike in their quest for mastery and insights. project page |
|
|
(2023) Sitthatka Jarussang, Thanik Pimpiban and Thanapong Intharah The KKU Herbarium Metaverse is a virtual simulation of the physical herbarium, offering a way to disseminate knowledge about plant diversity to a wider audience through an interactive platform that can display unlimited exhibition spaces and models of flowers regardless of the season, using photogrammetry techniques to create 3D models. project page / Metaverse |
|
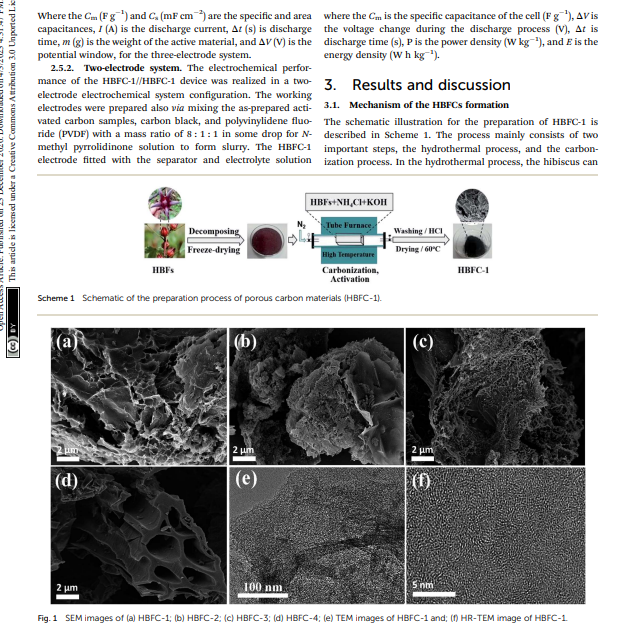
(2023) Kittikhun Kiattisaksiri, Chayakon Chanlun and Thanapong Intharah [Final round: NSC 2023] The development of a machine learning model for estimating the specific surface area (BET surface area) of carbon from plants using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) images through deep learning is now available as a web application for predicting the BET surface area value, aiding in the use of renewable energy storage devices. project page / publication / paper lists |
|
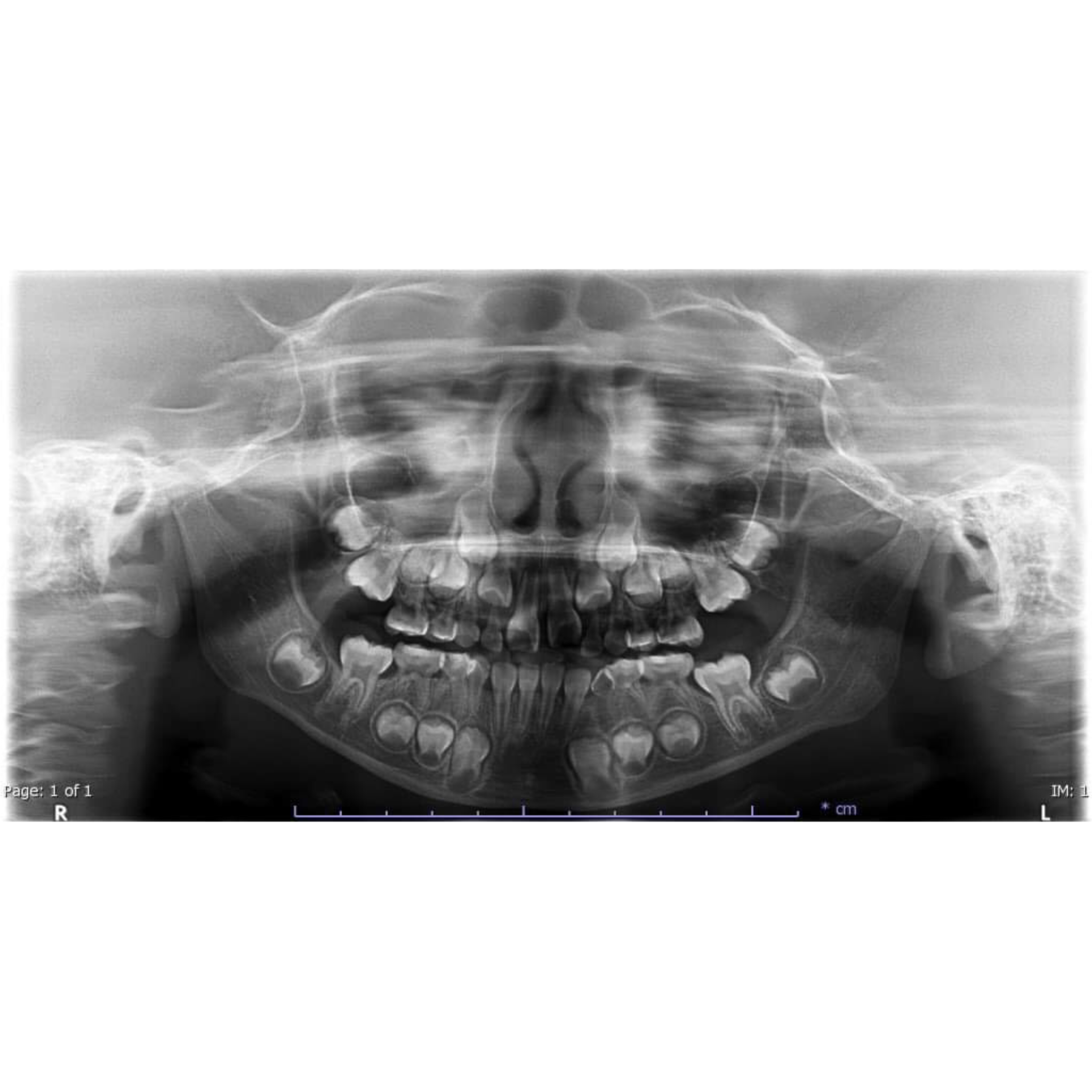
(2023) Wanita Somdej, Athitiya Thamavongsa and Thanapong Intharah [Honorable Mention: NSC 2023] A system for determining human age from panoramic radiographs has been developed using deep learning techniques, resulting in a web application that is faster, more accurate, and reduces dental errors in diagnostic planning, dental and orthodontic treatment, and forensic identification. project page / publication |

|
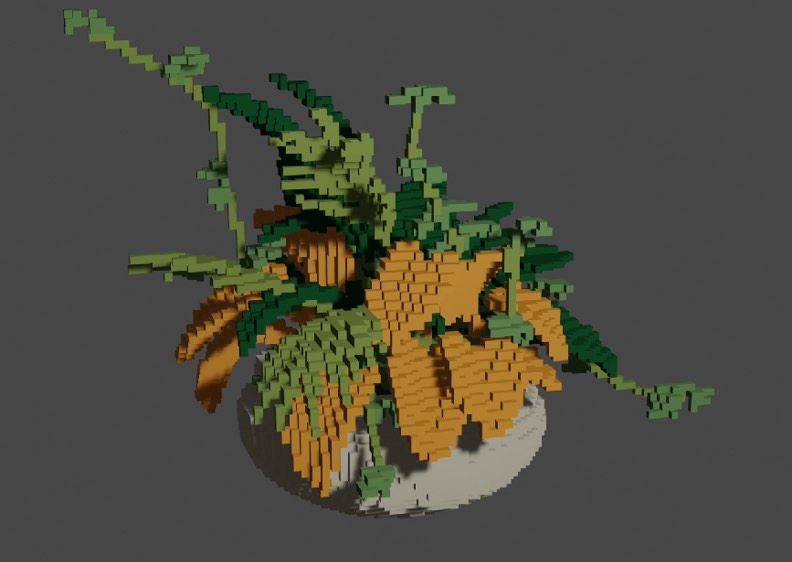
(2023) Jittakorn Chanthasi, Naruemon Saisophon and Thanapong Intharah We developed a web application that converts 3D models into voxel models with texture colors based on the color of the input models, for use in platforms such as game assets and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), providing the benefit of having voxel models with the same texture color as the input model. project page |

|
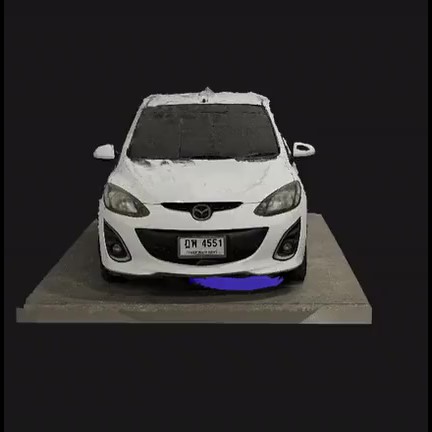
(2023) Supidchaya Tangkidwanich, Umaporn Kamphichai and Thanapong Intharah We developed a web application for estimating car parts and their damage level using deep learning. project page |

|
(2022) Chakrit Kammason and Thanapong Intharah In this work, we propose dual image QR codes that aim to improve QR code capacity and appearance while preserving the ability to be able to scan by standard QR code readers. project page / publication |
|
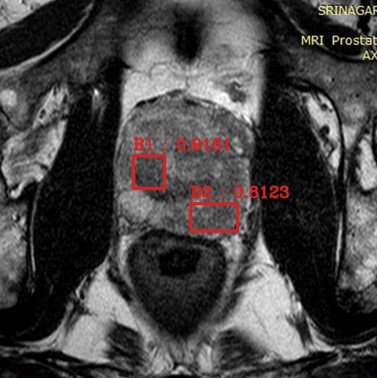
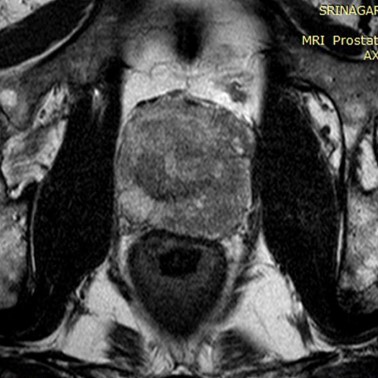
(2022) Kannika Wiratchawa, Yupaporn Wanna, Sirirat Cha-in, Chalida Aphinives, Potchavit Aphinives, Thanapong Intharah This work focused on detecting prostate cancer lesions in MRI images where the size of the dataset is comparatively small. project page / publication |

|
(2022) Kroravit Tharangsri, Thanapon Tayotee, Thanadol Chainet, Pharamut Markjarun, Thanapong Intharah In this work, we developed an end-to-end car damage estimation system via mobile camera. To estimate the damage, we first build 3D models of a car with images from a mobile camera and compared the model through CNN. part1: 3D model reconstruction / part2: Compare 3D Models |
|
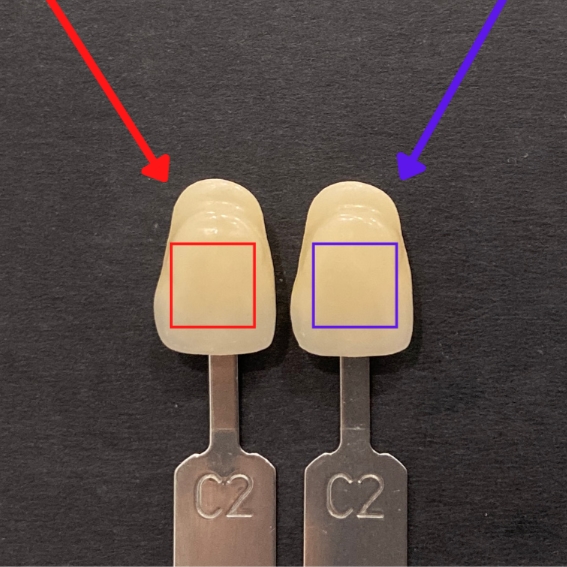
(2022) Waraporn Sittiwong, Rattaporn Leenaracharoongruang, Thanapong Intharah [Silver medal: Thailand Research Expo 2022] We proposed a new method to estimate shade of the denture with a mobile phone camera through the power of machine learning. report / code / publication |

|
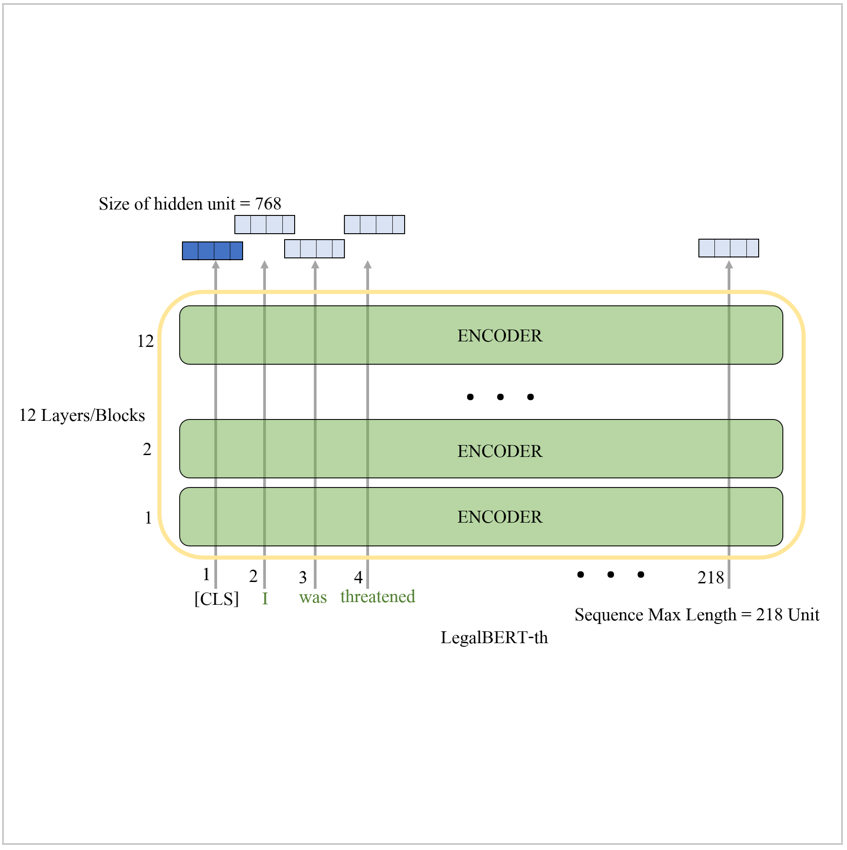
(2021) Kannika Wiratchawa, Tanutcha Khunthong, Thanapong Intharah [Silver medal: YRSS Award 2021] Tagging questions according to their topics is useful for internet forum management. In this work, we use the Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) model to categorize posts from Thai legal internet forums. report / video / dataset / code |

|
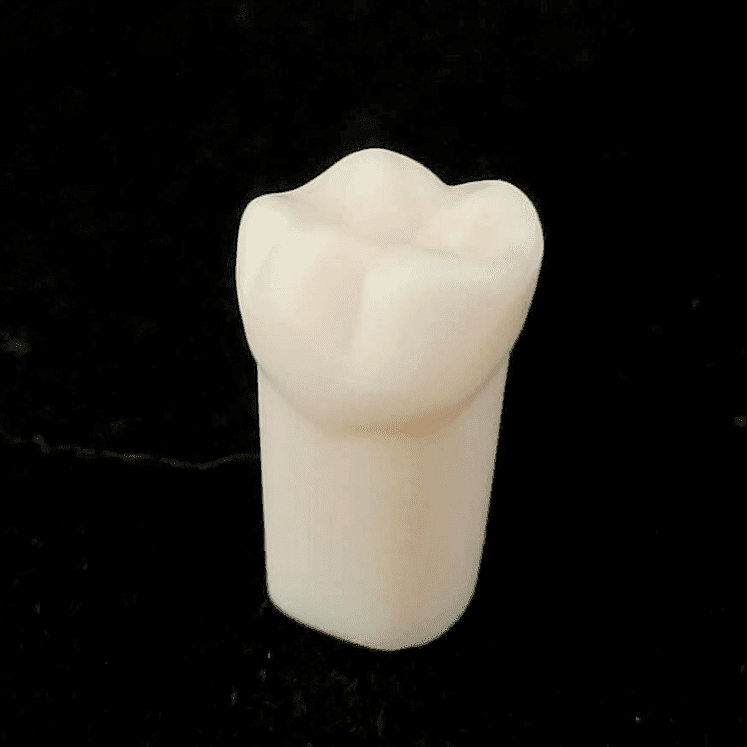
(2021) Phornpirom Lojarat, Thachamin siangeung, Supanita Daduan, Piyaphong Panpisut, Thanapong Intharah [Honorable Mention: NSC 2021] [Finalists Startup Thailand League 2021] We applied Photogrammetry technique to build models of plastic tooth to help dental students pratice Prosthodontics. report / video / dataset / code |

|
(2020) Yupaporn Wanna, Pimonpun Chachomphon, Haemwaan Sivarakst, Thanapong Intharah [2nd place: NSC 2020] [1st place: Priminister Digital Award 2020] (2021) Phattarawat Jaitiang, Nattharit Sawetwaranont, Thanapong Intharah We developed a dataset by scraping from YouTube and manually annotated them. We then train an AI to detect persons who concealed when they entered the scene. project page / dataset |
|
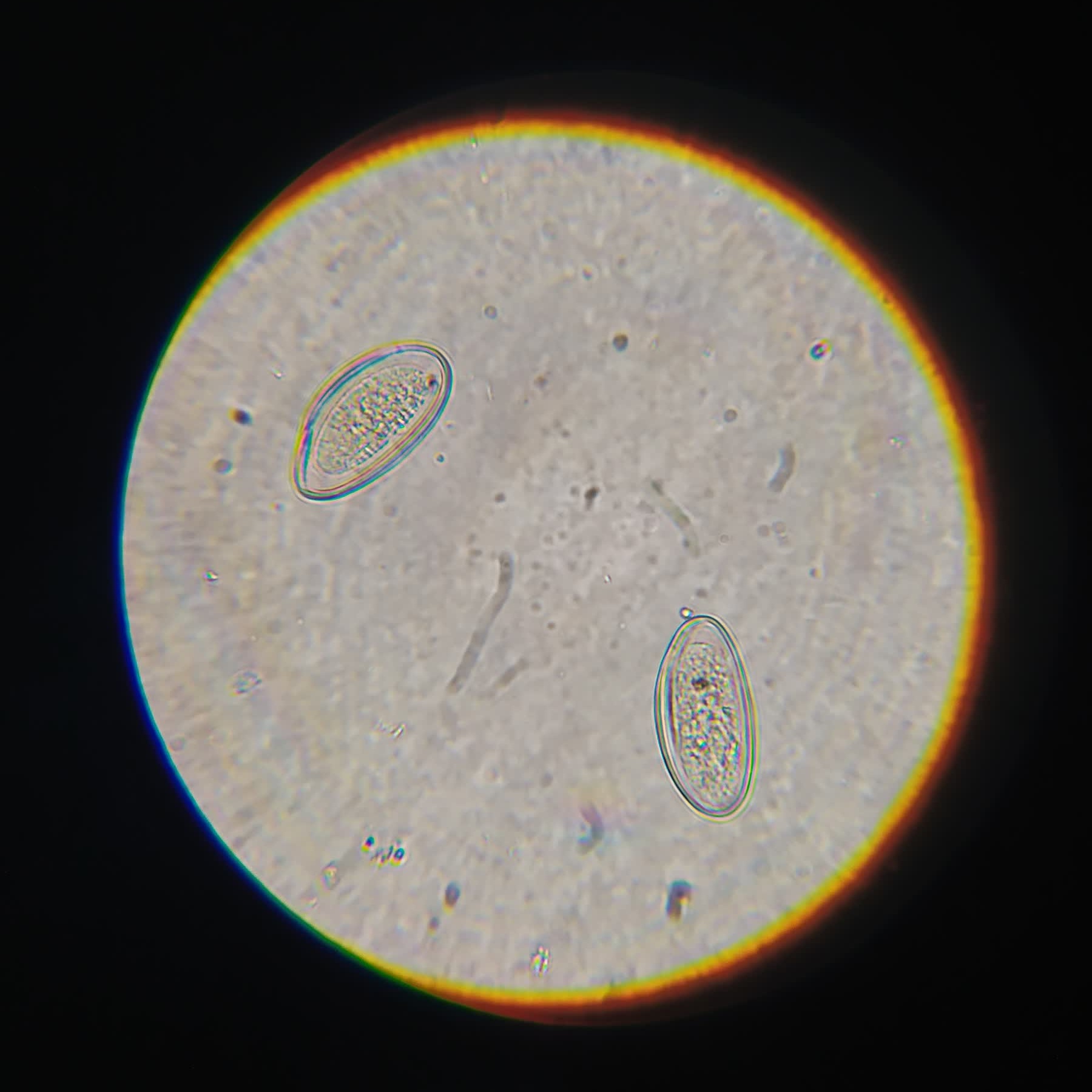
(2020) Chanikan Phadungkit, Siriwan Thanachitboon, Anchalee Techasen, Thanapong Intharah [Final round: NSC 2020] [Bronze medal: YRSS Award 2020] (2021) Jantraphon Somsuay, Mutita Butakhiaw, Yaowaluk Sompong, Anchalee Techasen, Thanapong Intharah [Final round: NSC 2021] We developed a chatbot to help associated medical science students learn about 7 medically important parasite eggs. report / video / dataset / code |

|
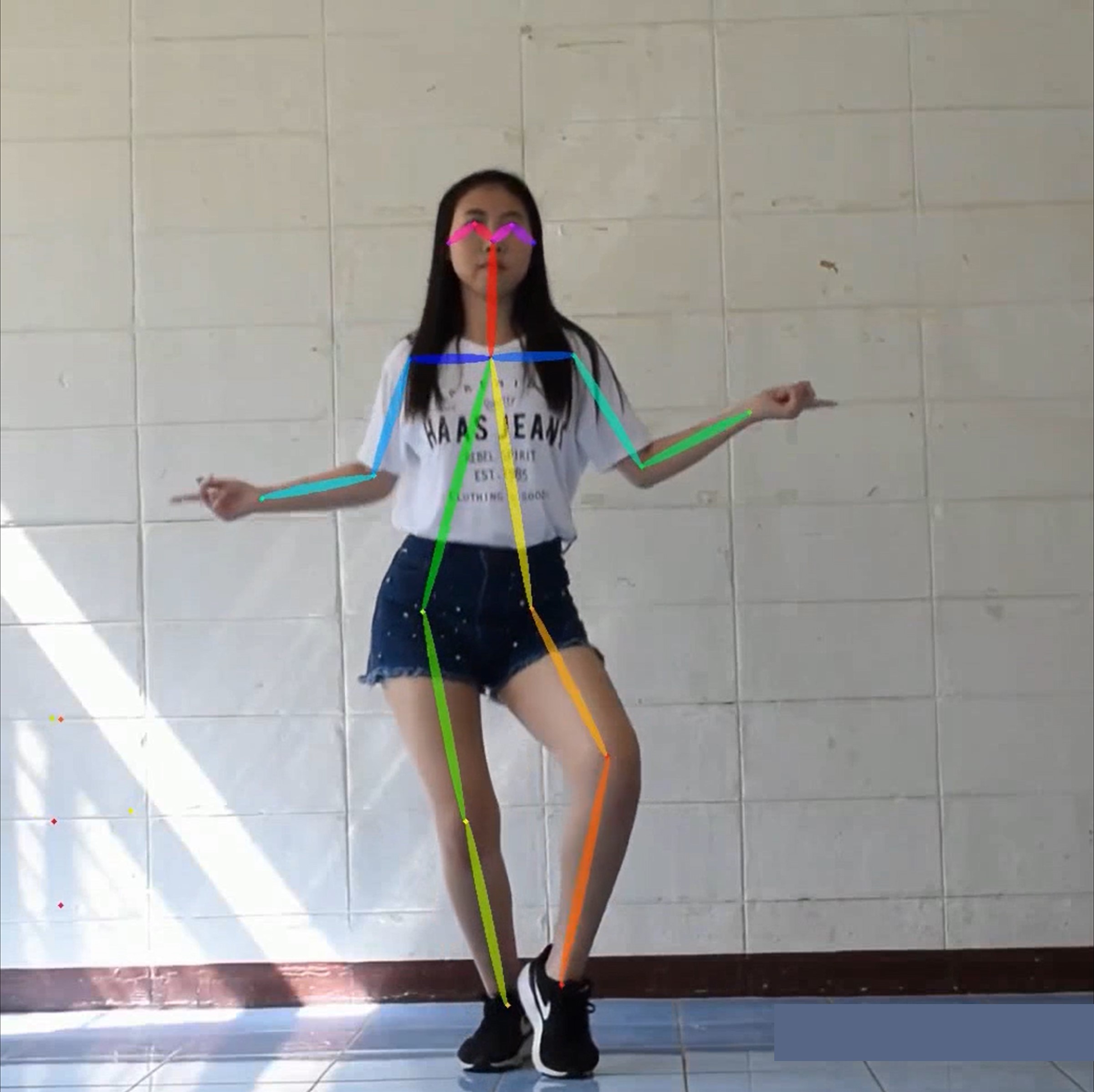
(2020) Sirirat Cha-in, Pakinee Kriamthaisong, Nattachai Watcharapinchai, Sitapa Rujikietgumjorn, Thanapong Intharah We developed a korean cover dance dataset and a pose evaluation technique to evaluate dance imitation score report / dataset / code |